Förderjahr / / ProjektID: / Projekt: Do we need computation offloading?
Computation offloading is a task of sending computation- and data-intensive application components to a resource-rich remote infrastructure for the execution.
Yes we do!
Smart phones, wearable watches and other IoT devices are constantly improved and are getting more sophisticated and powerful by every day. Therefore some may argue: Why do we even need then to offload the computation from a mobile device to the remote server for the execution?
Mostly because, technological evolution of mobile user equipment (UE) with increasing hardware capabilities and faster processors, is followed by an increasing amount of services coming with the advent of complex applications.
Therefore, when it comes to running new sophisticated resource-intensive applications such as augmented/virtual reality, voice/image/face recognition or interactive gaming, UE is still constrained. These constraint are mostly in the UE weight, size, limited battery lifetime, heat dissipation, storage and processing capabilities.
When running the resource-intensive applications
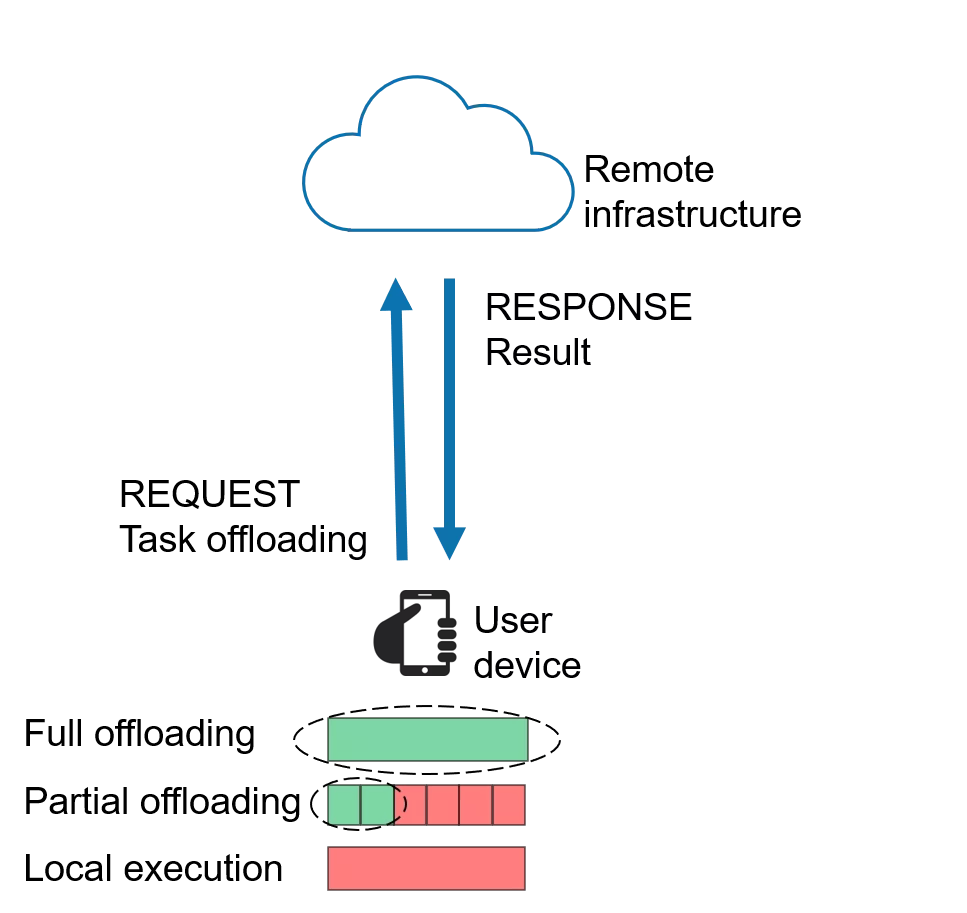
In order to enable such demanding applications on UEs and to extend their battery life time, task offloading to the Cloud/Edge has been introduced. As shown on Figure 1, the offloading consist of the following steps: i) request (transmission of the offloaded task to the remote infrastructure), ii) task processing at the remote infrastructure and iii) response (transmission of the results back to the UE). Considering the availability of resources and application complexity, following offloading decisions can be made. First, local execution where the whole computation is done locally at the UE; then full offloading with the whole computation offloaded and processed by the remote infrastructure; and finally, partial offloading where some parts of the computation are processed locally at UE and the rest is offloaded to the remote Cloud/Edge infrastructure.
Offloading on the Edge resources
Offloading time and consequently the application performance is strongly affected by the issue of transmission time. Therefore we consider Edge offloading, that is a process of offloading tasks to the nearby Edge infrastructure for applications with the real-time restrictions. Edge servers are located in single-hop proximity to mobile devices and therefore can answer the processing and analysis requirements in a timely manner, extend UE battery lifetime and improve their storage and computation capabilities. Beside a decision whether to offload or not (full/partial offloading or local execution), when and where (Cloud/Edge infrastructure), a challenge in Edge offloading is how to choose on which Edge node to offload the application execution. In the following blog posts we will answer this challenge considering the minimum application execution time and Quality of a Service perceived by the end user.


